Did you learn something new? Share with a friend!

You’ve learned you need a business plan to help get your small business going. But what exactly is the business planning process?
You might be wondering: How do you write a business plan? What needs to go into it? Is it even really necessary?
The business planning process is the methodical approach of creating a business plan that will help you get your business off the ground. If you’re starting a small business or looking to get more funding for an existing one, it’s something you’re going to want to know how to do.
In this article, we’ll walk you through all the steps of the business planning process, so you can create a killer business plan that will help you set your business up for success.
Let’s get to it!
Disclosure: Our website participates in various affiliate marketing programs, which means we may earn a commission on purchases made through our affiliate links. We only promote products and services that we believe offer value to small business owners. Just as a quick reminder, the following information is not legal advice. Be sure to speak with a local attorney before making any legal decisions.
Quick Links
- What is a Business Plan
- Why You Need a Business Plan
- Business Planning Software
- Business Plan Formats
- Business Plan Components
- The Business Planning Process
- Tips for Writing a Killer Business Plan
- Common Mistakes in the Business Planning Process
- FAQs About the Business Planning Process
- What’s Next After the Business Planning Process
What is a Business Plan
Before we dive into the business planning process, it’s important to understand what a business plan is. A business plan is a written document that outlines your business idea, operations and strategy, financial projections, and marketing plans.
It serves as a roadmap for the business to follow, providing guidance on how to achieve success in the marketplace. It also helps you make better business decisions by allowing you to assess different options before settling on one course of action.
Why You Need a Business Plan
If you’ve done any research into how to start a small business, you’ll see a lot of recommendations for creating a solid business plan, and for good reason. Let’s talk about why having a business plan is so important.
Funding
One of the biggest reasons people decide to create a business plan is to get more money for their business. If you plan to apply for a loan from a bank or another financial institution, they’re going to want to see your business plan.
Because your business plan outlines the potential future and success of your business, it helps give the bank a good idea of whether or not you’ll eventually be able to pay the loan back. A business that doesn’t have a good plan or isn’t very viable isn’t a very good investment on the bank’s part.
This is why having a well-written business plan can be so important when it comes to getting the funding you need for your business.
Organization and Focus
Creating a business plan forces you to really look at the ins and outs of your business and evaluate different aspects in detail. You can work through a lot of potential problems or hurdles in your business well ahead of time by identifying them during the business planning process.
Having a business plan also helps you set goals for the business and create processes that will help you reach those goals. You’ll be able to outline things like marketing, the structure of your business, revenue goals, and more.
This will help you define the strategies that you’ll use to build your business over the first few years. Considering how many businesses fail in the first few years, having a business plan in place can really help you have a better chance of success.
Decision-making
Another reason the business planning process is so important is that your business plan will help you make important decisions about your business. You’ll decide how to allocate funds, what products or services to offer, and how you’ll expand your business in the future.
By having all of this information laid out in a business plan ahead of time, it can help you make decisions faster and more confidently. You’ll be able to look at the business plan and determine whether something is a good fit for your business or not.

Business Planning Software
Now that we’ve fully covered why you don’t want to skip creating a business plan, let’s talk about actually writing one. Although it’s clearly worth the effort, it’s not an easy task.
I’ll go on record and say that if you have the funds to do so, you can save yourself a lot of time and effort by using a company that offers business planning software.
Business planning software is a type of computer program that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create, manage, and update a business plan. This software typically provides a step-by-step process for developing a comprehensive plan.
Some common features of business planning software include:
- Financial projections: The software can help create financial projections for your business, including projected income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Templates and samples: Many business planning software programs come with pre-designed templates and sample plans that you can customize to fit your business.
- Collaboration tools: Some business planning software programs include collaboration tools, allowing multiple users to work on the same plan simultaneously and share information and ideas.
- Planning and strategy tools: The software can help you create a strategic plan, including defining your target market, determining your unique selling proposition, and creating a marketing plan.
- Investment tracking: Some business planning software programs can help you track investments and returns, providing valuable information for investors and other stakeholders.
- Presentation tools: Some business planning software programs have presentation tools, allowing you to create professional-looking presentations and share your plan with others.
Overall, business planning software can help streamline the process of creating a business plan and make it easier to keep your plan up-to-date as your business evolves.
Our Top Picks for Business Planning Software
Here are our top picks for software to help speed up the business planning process:
Wrike: Wrike is a project management software that offers an intuitive drag-and-drop interface for creating business plans. It also provides templates and samples to make the process easier, as well as collaboration tools so multiple people can work on the same plan at the same time.
LivePlan: LivePlan is a business planning software program that helps you create comprehensive business plans. It includes financial projections, templates and samples, collaboration tools, and presentation tools.
Bizplan: Bizplan is business planning software that offers everything from business plan templates to investor tracking and even pitch deck creation. It also offers collaboration tools so multiple people can work on the business plan at the same time.
Enloop: Enloop is business planning software that helps entrepreneurs create business plans quickly and easily. It includes financial projections, templates, samples, and collaboration tools.
Business Sorter: Business Sorter is business planning software that helps business owners create business plans by answering questions and filling out forms. It also offers templates and samples, as well as collaboration tools for multiple users to work on the same plan.
No matter which business planning software you choose, using one of these programs can help simplify the business planning process and enable you to create a comprehensive business plan quickly and easily.

Business Plan Formats
Whether you decide to use business planning software or write it yourself, one of the things it’s important to decide ahead of time is what format you’ll be using for your business plan.
The most common business plan formats include:
Traditional
Traditional business plans are typically long documents that cover all aspects of the business. They include sections on business overview, market analysis, competitive analysis, product/service description, business model, operations plan, management team, and financial projections.
Traditional business plans are very detailed and lengthy and require extensive research. The extra level of detail can take more time, but it makes them much more useful for things like securing funding or loans.
Lean
Another format for your business plan is the lean business plan. These plans are a lighter version of traditional business plans and focus more on the core elements of your business.
Instead of a lengthy document, a lean business plan typically consists of a one-page summary of key business concepts, such as the value proposition, target market, and revenue streams. The focus is on testing and validating the key assumptions of the business, rather than producing a comprehensive plan.
Pitch decks
Pitch decks are business plans for entrepreneurs who want to present their business ideas to investors. They typically consist of 15-20 slides that include an overview of the business, market research, competitive analysis, product/service description, business model, team information, and financial projections.
The focus is on creating a concise presentation that will help convince investors to invest in the business. Pitch decks are usually shorter and easier to create than traditional business plans.
No matter which format you choose, it’s important that your business plan is clear, concise, and well-researched so potential investors can see the value of investing in your business.
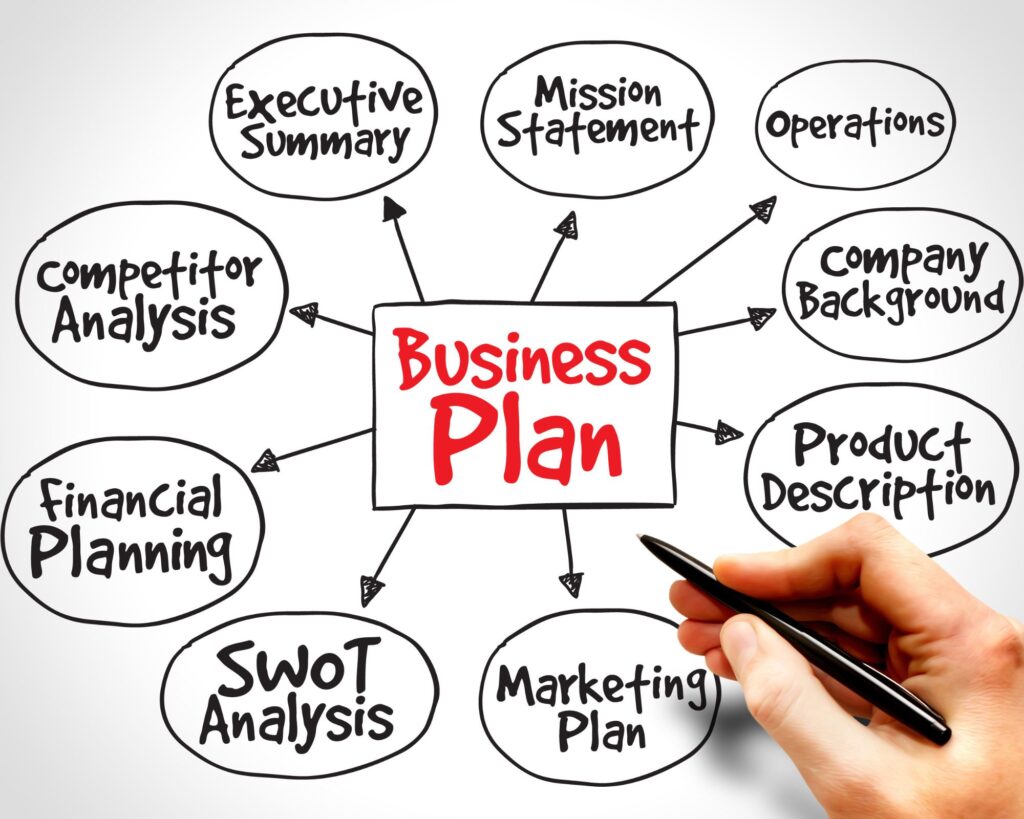
Business Plan Components
Now, let’s talk about what actually goes into your business plan. During the business planning process, you’ll want to make sure that you research and fully understand each of the following components:
Executive Summary
The first part of your business plan will be the executive summary. This is a crucial part of your business plan because it’s often the first section that potential investors or lenders will read.
This, in essence, is where you put your company description. Help potential investors understand what your business is all about.
A well-written executive summary should include the following elements:
- Overview of the business: A brief description of the business, including its products or services, target market, and mission statement.
- Problem and solution: A description of the problem the business is trying to solve and how it plans to solve it.
- Unique selling proposition: A description of what sets the business apart from its competitors and why customers should choose it over other options.
- Market opportunity: An overview of the size and potential of the target market, including demographic and psychographic information.
- Marketing and sales strategy: A description of how the business plans to reach and sell to its target market, including its marketing channels and sales tactics.
- Financial projections: A summary of the key financial projections, including revenue, profit, and cash flow projections.
- Management team: A brief overview of the key members of the management team, including their qualifications and experience.
- Request for funding: If the business plan is being used to secure funding, the executive summary should include a request for funding and a brief explanation of how the funds will be used.
The executive summary is a high-level overview of your business that covers the main points and should be no more than 2 pages. Later on, in the business plan, you’ll go into more detail with each of the elements, but right now you’re just trying to give a quick snapshot for the reader.
Your summary should be brief enough to read in a few minutes, but comprehensive enough to provide a complete picture of the business. It’s a good idea to write the executive summary last, after you’ve written the rest of the business plan, to make sure it fully summarizes what’s included in the rest of your plan.
Industry or Market Analysis
The next thing you’ll want to cover in the business planning process is market analysis. This is the section of your business plan where you cover information on the target market (who you’re trying to sell to), the competition (who else is doing what you’re doing), and overall industry trends (what’s happening in similar businesses overall).
A market analysis should include the following elements:
- Industry analysis: An overview of the industry, including its size, growth rate, and key trends.
- Market segmentation: A description of the people you’re hoping will purchase your products/services, including demographic, geographic, and psychographic information.
- Customer analysis: A description of the target customer, including their needs, motivations, and buying habits.
- Competition analysis: An analysis of the competition, including their strengths and weaknesses, market share, and key things that set their business apart.
- Market size and growth: An estimation of the size of the target market and its growth potential, based on available data and industry trends.
- Market trends: An overview of key trends in the industry, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, and emerging opportunities.
- SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis, which stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, provides a comprehensive overview of the market and the business.
The market analysis should be based on reliable data and research and should provide a clear and accurate picture of the target market and the industry. Don’t just guess. This is an area where it pays to make sure you really do your research.
The information you put in this section will go a long way toward making marketing decisions and making sure your business is set up for success from the beginning.
Product/Service Line
The next part of the business planning process will be describing the product or service you’re going to offer. This is where you get a chance to explain how your business will help solve the problem of your dream customer.
How will you help the people who will buy from you? What sets you apart from your competitors? What’s your competitive advantage?
This section should include the following elements:
- Product/service description: A detailed description of each product or service offered by the business, including its features, benefits, and unique selling points.
- Product/service development: A description of the product development process, including research and development, testing, and product launch. Be clear on how you will create your product and deliver it to your customers.
- Intellectual property: A description of any intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights, related to the products or services offered by the business.
Make sure this section is clear, concise, and focused on the unique selling points of your products or services. Understanding how your business is different from what’s already on the market will become a great selling point in your marketing strategies.
Marketing, Sales, & Product Plan
The next part of the business planning process is getting super clear about your marketing and sales strategies. This is where you cover how you’re going to actually sell your product or services.
The goal of every successful business is getting their product in front of the people who actually want to buy it. This is the section of your business plan where you explain exactly how you’re going to do that.
This section should include the following elements:
- Target market: Recap who you’re selling to, including demographic, geographic, and psychographic information.
- Market segmentation: A description of how the target market has been segmented into smaller, more specific groups based on factors such as age, income, and interests. Within your broader target market, what are the smaller groups you’ll be selling to?
- Product/service positioning: A description of how the products or services offered by the business will be positioned in the market, including the unique selling points and benefits. Are you the most unique, cheapest, fastest, most skilled, etc? In what way is your product better than what’s already out there?
- Marketing mix: A description of what you’ll be using to persuade your ideal customer to buy from you. This includes the product (what you’re selling), price (pricing strategy, discount, payment terms), place (where are you selling it), and promotion strategies (how will you reach your customers) for each product or service.
- Marketing channels: A description of the marketing channels the business will use to reach its target market, including advertising, public relations, direct marketing, and sales promotions.
- Sales strategy: A description of the sales strategy, including how the business will generate leads, close deals, and maintain customer relationships.
- Marketing budget: A description of the marketing budget, including projections for advertising, promotions, and other marketing expenses.
This section of your business plan is another area where you don’t want to skimp on the research. You want actual facts and data to help determine your marketing strategies.
Getting your products and services in front of the right people is going to make or break your business, so make sure to give this section the attention it deserves.
Operating Plan
The next part of the business planning process is writing the operating plan. This section is where you create a detailed description of how the business will operate on a day-to-day basis.
It includes the following elements:
- Organizational structure: A description of the structure of the business, including the ownership, management, and employee roles and responsibilities.
- Physical location: A description of the physical location of the business, including the size, layout, and facilities. If you’ll be selling online, describe where and how.
- Equipment and supplies: A description of the equipment and supplies needed to operate the business, including any special requirements and costs.
- Production process: A description of the production process, including the steps involved in creating the products or services offered by the business.
- Quality control: A description of the quality control procedures used to ensure that the products or services offered by the business meet the standards and expectations of the target market.
- Inventory management: A description of the inventory management system used to track the products or services offered by the business, including the methods used to track inventory levels, reorder points, and lead times.
- Supplier relationships: A description of the relationships with suppliers, including the terms of the agreements, the types of products or services purchased, and the payment terms.
- Operating expenses: A detailed list of the operating expenses of the business, including rent, utilities, payroll, insurance, and other expenses.
With this section, just do your best to provide a clear picture of how the business will operate on a day-to-day basis.
Financial Plan
The next part of the business planning process is what most people think of when they think of writing a business plan – the financial plan. This is where you include how much money the business is going to cost and how much you think it’s going to earn.
This section should include the following elements:
- Projected income statement: A projection of the business’s revenue, costs, and expenses over a specified period of time, typically 3 to 5 years.
- Projected balance sheet: A projection of the business’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specified point in time.
- Projected cash flow statement: An estimation of the money coming into and going out of your business over a period of time.
- Break-even analysis: An analysis of the point at which the business’s revenue will equal its expenses, indicating the point at which the business will become profitable.
- Capital requirements: An estimate of the amount of money required to start and run the business, including the sources of capital and the terms of any loans or investments.
- Sensitivity analysis: An analysis of the impact of changes in the market, the economy, and the business on the financial projections.
- Risk assessment: An assessment of the risks faced by the business, including market, operational, financial, and regulatory risks.
This is another section of the business plan where you really want to do your research. Anyone you’re hoping to secure funding from is going to pay special care to this section of your business plan.
It needs to be based on accurate and realistic assumptions about the market, the economy, and the business.
Appendix
The last part of the business planning process is putting together the appendix. The appendix contains additional information or materials that support the content of the business plan.
This information is typically not essential to the main body of the business plan, but is included for reference or to provide additional detail. It includes supporting documents and data, such as resumes of key personnel, market research, financial statements, product samples, and contracts.
The appendix is usually located at the end of the business plan and isn’t typically read by investors or lenders unless they need additional information or clarification on a specific issue. But you’ll still want to make sure that it’s well-organized and clearly labeled for easy reference.
Related posts:
- 9 Quick Tips for Generating a Successful Business Idea
- 14 Options for Business Capital Funding: How to Get Funding for Your Small Business
- How to Come Up With a Brand Name That Attracts Customers
- Why Digital Marketing is Important for Small Business: What You Need to Know

The Business Planning Process
Now that we understand what all goes into a business plan, let’s take a look at the business planning process now and understand how to pull all the parts of your business plan together.
Step 1: Do your research
Before you start writing your business plan, you’ll want to do some research. Research the market, the economy, and relevant business trends.
Look into competitors and analyze their business models. Talk to potential customers or clients about what they want in a business like yours.
The more research you do, the easier it will be to write your plan and the better chance you have of securing funding.
Also, make sure to cite your sources during this stage so you can include them if needed to back up your information and strategies.
Step 2: Strategize
Once you’re done researching, it’s time for strategic planning. This is where you decide on the business model and business strategies that will make your business successful.
What’s the best marketing strategy for your ideal customer? How do you highlight what your business does well?
How will you fix or avoid any potential threats or risks to your business?
Identify key business objectives that will help you reach your goals, create a timeline for reaching milestones, and plan out your activities, resources, and budget.
Step 3: Financial Forecast
Once you have your strategies in place, it’s time to start looking at how much everything is going to cost. This is where your business plan’s financial projections come in.
Take some time to figure out how much it’s going to cost to get your business up and running. How long until you’ll be making a profit?
How much will you need to price your product or services in order to continue making a profit?
What do your business expenses look like for the first year? What about the first three years?
Take all of that information and put it into spreadsheets, graphs, and charts to make it easier to read and understand.
Step 4: Draft your plan
Now you’re ready to write your plan! Take all of the research, data, strategies, and plans you’ve developed and put them into your business plan.
The easiest thing to do is to take the components listed above step-by-step and start filling out each section. Be sure to leave the executive summary for last, so you can make sure you’re truly summarizing all the details of your business plan.
Step 5: Revise and Proofread
Once you’ve got your first draft done you’ll want to start revising it. Take some time to proofread your plan.
Are there any typos or errors that need to be corrected? Did you cite your sources?
Did you cover all the elements of a business plan? Is it clear, concise, and easy to read?
Have your business partners, mentors, or advisors look at it and ask them for their feedback. Make sure you address any issues they bring up in the revisions.
Step 6: Practice your presentation
Once you’ve gotten your business plan written, it’s time to practice your presentation. Rehearse your business plan presentation in front of friends, family, business partners, or potential investors.
This will give you a chance to see how well you can explain the business plan and answer any questions that come up. It will also help you identify areas that need more explanation and sections of the business plan that don’t make sense.
These steps will help you through the business planning process and make sure your business plan is complete and accurate. When it comes time to present your business plan, you’ll have a well-thought-out document that makes an impact on potential investors or business partners.

Tips for Writing a Killer Business Plan
Here are some tips that will help with the business planning process:
Be clear and concise – use clear and simple language
A business plan should be concise and focused, avoiding unnecessary details. The length of a business plan varies, but it should not exceed 20-30 pages.
Avoid using complex jargon or technical language, and instead, use clear and simple language that everyone can understand. Remember, you’re trying to convince someone about the potential success of your business.
If they don’t understand half of what you’re talking about, they aren’t going to see much of a future for your business.
Don’t skimp on the research
I’ve said this more than a few times, but it’s worth repeating. Don’t skimp on the research!
You want the information and data you present in your business plan to be based on facts, not guesswork. If your research seems insufficient or untrustworthy, potential investors won’t have enough information to make an informed decision about your business.
Not to mention, if you don’t properly research the market before launching your business, it could end up costing you more in the long run.
Be realistic
Another good tip to keep in mind when writing your business plan is that you need to be realistic. Don’t over-inflate your business’s potential or make promises that you can’t keep.
Setting realistic goals and expectations will help you stay focused on what needs to be done, as well as give investors a more accurate sense of what they’re getting into.
Remember, your business plan isn’t just a way to get investors, it’s also a plan for how you’ll run your business over the next few years. You don’t want that plan based on how you “hope” things are going to go.
It needs to be based on realistic data and research to give your business the best chance of success.
Get feedback from others
Getting feedback from business mentors and advisors is a great way to make sure your business plan is complete and accurate. Having others who have experience in business look over your business plan can help you catch any mistakes or areas of improvement that you may have missed.
It also allows you to get insight and advice from people who have been in business before, so you can use their knowledge and expertise to help guide your business decisions.
Make it flexible
Something else you’ll want to keep in mind is that you want your business plan to be flexible. Wherever possible, don’t get too attached to specific details about your business.
As you start digging into the research, you might find areas and things that need to be tweaked or changed. Rather than trying to stick to a business plan that doesn’t fit the business anymore, be willing to make changes and be flexible with what you’re presenting.
The business planning process is an iterative one and you should always be open to making adjustments as needed.
Make it visually appealing
Another good tip to keep in mind during the business planning process is that you want it to be visually appealing. We mentioned that your business plan shouldn’t be more than 20-30 pages.
Do you want to slog through 20-30 pages of nothing but text? Probably not, right? Well, the investors or lenders who read through several of these a day probably don’t either.
Make the information more accessible by using charts, graphs, and other visual aids to illustrate important points. You want to make sure your business plan makes a good impression, so don’t be afraid to invest in making it look as good as possible.
Common Mistakes in the Business Planning Process
The business planning process can be a bit in-depth and it’s easy to make a few mistakes along the way. Here are some common mistakes you want to avoid while writing your business plan:
Bad business idea
The first, obvious mistake is having a bad business idea. A bad business idea isn’t going to be successful and is probably going to waste a lot of time and effort researching it.
You want to make sure that the business you’re proposing has a strong business model, realistic growth potential, and is something you are passionate about and can succeed in.
If you haven’t yet, check out our article on generating a business idea so that you can ensure that your business plan is based on an idea with potential.
No exit strategy for investors
Another common mistake people make when writing a business plan is not having an exit strategy for investors. If you are looking for investors, you need to include a plan on how and when they will be able to get their investment back.
Having an exit strategy shows that you have thought through the business model and potential risks, making it more likely that investors will consider giving money to your business.
Unbalanced teams
Another mistake business planners make is having an unbalanced team. Your business plan should include the skill sets of each of your business partners and how those skills will benefit the business.
You don’t want to have a business that has too many people in one area (like marketing or web development), but not enough in other areas (like operations or accounting). Make sure that each business partner is bringing something useful to the business, and that they are all contributing equally.
Missing financial projections
A big mistake people often make during the business planning process is not including enough information in the financial projections section.
It’s not enough to just say that the business will make money. You need to include detailed information about how much money you expect the business to make in the first three years, as well as any potential risks or uncertainties associated with those numbers.
And you need to show how the business will make that money. How much will you charge? What is the cost of making the product?
How many customers do you need and how do you plan on getting them?
All of this information needs to be included and backed up by research so potential investors can feel confident in the future of your business.
Spelling and grammar mistakes
Finally, business plans should be free of any spelling and grammar mistakes. This is a business plan that you are sending to potential investors or lenders.
You want to make sure the document looks professional and polished, so don’t forget to double-check your spelling and grammar before submitting it.
Being able to spell and write well might not have anything to do with the business you’re trying to start, but it will go a long way toward inspiring trust and confidence with any potential investors.

FAQs About the Business Planning Process
Here are some frequently asked questions about the business planning process:
How long should a business plan take?
It depends on the complexity of your business. Generally, business plans can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months to write.
What is a good business plan?
A good business plan is one that includes a detailed business model, realistic financial projections, an exit strategy for investors, and a balanced team.
What’s the purpose of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are: to clarify your plans for growth, to understand your financial needs, and to attract funding from investors, banks, and lenders.
What are the different types of business plans?
The two most common types of business plans are traditional business plans and Lean business plans. A Lean business plan is shorter and more focused than a traditional business plan. It focuses on what’s essential for the business and allows for quicker iterations.
What’s Next After the Business Planning Process
I hope this article has been helpful in guiding you through the business planning process. Once your business plan is complete, you can move forward with launching and growing your business.
You’ll need to create marketing strategies, find funding sources, and secure partnerships that will help get your business off the ground. There may also be legal considerations such as setting up business accounts, filing business taxes, and applying for business licenses.
Check out our Start Your Business page for more resources to help you with the next steps in your business!
Read LessYou might also like…

9 Quick Tips for Generating a Successful Business Idea
Ready to take the leap into entrepreneurship, but need some help generating a business idea? We’ve got you covered! Read more

14 Options for Business Capital Funding: How to Get Funding for Your Small Business
Trying to get your small business off the ground? Check out these 14 options for business capital funding! Read more
Legal Forms of Business: How to Choose the Right Business Structure
Learn about the different legal forms of business, from sole proprietorships to corporations and everything in between. Read more

Looking for Your First Customer? Try These 10 Proven Strategies
Ready to get your business off the ground? Here are 10 proven strategies to help you find your first customer. Learn More
